How To Know What Camera Lens To Have

Apertures, focal lengths, ƒ-stops -- with all the terms surrounding camera lenses, it's completely normal for a new photographer with an interchangeable-lens photographic camera to feel out of their depth of field and lost in a circle of confusion.
Simply accept no fear, the purpose of this commodity is to give you an overview of camera lenses -- the terms yous need to know, how they do the special things they do, and in item, how they can exist relevant to the kinds of photographs you desire to make.
At the virtually basic level, it'due south worth understanding that for all their bells and whistles, the purpose of a lens is to focus the light from a scene and straight information technology towards the sensor in your photographic camera. There's a lot of technology inside a lens that affects how information technology does this, but ultimately, all lenses achieve the same goal.
Non all lenses are created equal
Lenses that even announced to be like in their names tin can offer dramatically different capabilities. For instance, a lens with paradigm stabilization born will help counteract the shakiness that just property the camera with your easily can induce, but it tin brand a lens more costly. A lens might have special macro functions that assist with taking very shut-up pictures. Yous'll take to decide whether these functions are worth the extra toll.
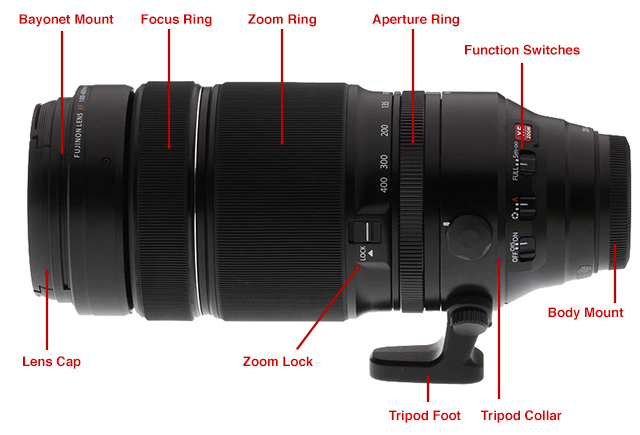
This photograph of a Fujinon XF 100-400mm f/4.five-five.6 R LM OIS WR lens demonstrates all of the parts of a lens (not all lenses volition have all these features).
- Body Mount:
- This is the office of the lens that attaches to the camera, using a mount designed to fit a specific brand of camera. Generally, one manufacturers' lens won't fit on a camera designed by another manufacturer.
- Role Switches:
- These switches let you lot to activate, deactivate, or otherwise alter features offered past the lens. For example, one of the switches on the above Fujinon lens allows you to activate or deactivate autofocus.
- Aperture Ring:
- Once a standard part of whatsoever photographic camera lens, the aperture ring is growing more and more uncommon on mod lenses. The ring allows yous to manually command the amount of low-cal hitting the sensor past opening and closing the discontinuity of the lens. All modernistic cameras let you to do this by selecting the aperture yous desire from the camera's interface.
- Zoom Ring:
- Not all camera lenses have this function, which allows yous to arrange the focal length of the lens -- these lenses are called "zoom lenses" considering they allow you to "zoom in" from a broad bending scene, getting closer to your field of study.
- Focus Ring:
- Y'all use this ring to adjust what is in focus for the photographic camera. Almost all modern cameras offer the ability to focus for you automatically, but in some cases, the camera can fail at this. For example, if it'south a dark scene, there might not exist enough light for the camera to autofocus, simply more than enough for yous to figure out what should exist in focus.
- Bayonet Mount:
- You can apply this part of the lens to attach a lens hood, which stops stray light from entering the lens and causing flare. Most modernistic lenses apply this bayonet mount design for lens hoods, though at that place are a few other attachment methods.
- Lens Cap:
- Attaching a protective cap to the front of the lens is a bang-up way to prevent impairment to the sensitive forepart glass element. Likewise, there is normally a threaded band near the front of the lens, onto which you can attach filters for a multifariousness of functional and artful effects.
- Zoom Lock:
- For some zoom lenses, over time, the zooming machinery tin can become a little loose, meaning that when the camera is pointed downwardly, the lens tin can zoom on its own. Using a zoom lock switch will prevent this.
- Tripod Human foot:
- This part of the lens is used to attach longer lenses to a tripod, to remainder the photographic camera-lens combination more safely. If you attached this long Fuji lens, for example, on a tripod just from the camera, at that place would be a lot of stress placed on the photographic camera's lens mountain.
- Tripod Collar:
- This part of the lens tin can rotate, allowing you to turn a photographic camera while it'south fastened to a tripod.
What is Focal Length?
Roughly stated, focal length refers to the amount of the scene that a lens captures. You would apply a wide-angle lens to capture more than of a scene, like what yous would run into in a landscape; a telephoto lens capture less of a scene, simply magnify subjects farther away, bringing them closer. Focal length is measured in millimeters, just this doesn't relate to the length of the lens. All you need to retrieve is that the longer the focal length, the narrower the angle of view and the higher the magnification. The shorter the focal length, the wider the bending of view and the lower the magnification.
For case, an 18mm lens is very much a wide-angle lens, while a 300mm lens would bring the scene much closer to yous.
You probably received your camera with a kit lens, with focal length ranges typically spanning moderate broad-angle to short telephoto. You'll probably be looking to buy a lens that corresponds to your shooting: If you've institute yourself wishing you could see more of a scene, you may want to consider a wide-angle lens. If you frequently wish you could zoom in to run across shut-up shots of faraway birds, wildlife, or your kids on a sports field, you lot'll probably be interested in a telephoto lens.

On the left, the Tamron 15-30mm ultra-wide-angle zoom lens. On the correct, the Nikon 300mm telephoto prime lens.
All about apertures
The aperture is the role of the lens which determines how much light is allowed to pass through to the sensor. Betwixt this, ISO and the camera's shutter, you'll be able to dictate how vivid or dark your captured paradigm volition be. An discontinuity is rated in ƒ-stops, a definition of which is a bit beyond the telescopic of this article. All you really need to know is that a low ƒ-stop number, like ƒ/2.eight, will let in more light than a loftier ƒ-stop number, similar ƒ/11.
If that hasn't confused you yet, it'due south worth noting that the process of moving from a low ƒ-stop number to a high ƒ-stop number is chosen "stopping down."
Some zoom lenses are equipped with a what's chosen a variable aperture, which is a design compromise to reduce the size and weight of the lens, not to mention the price. What this means is that equally the lens is zoomed in towards a longer focal length, the largest discontinuity size volition subtract, allowing less light to enter the camera. For instance, the Nikon 18-55mm ƒ/3.5-5.6 lens will offer an aperture of ƒ/iii.5 at the 18mm focal length, and ƒ/five.6 at the 55mm focal length. By contrast, the Nikon 17-55mm ƒ/2.8 lens volition offer a broad ƒ/ii.8 aperture regardless of what focal length you lot select. You get the maximum corporeality of calorie-free possible in the latter lens, only it's more than expensive, also as larger and heavier.
Usually, you'll select the aperture you want to apply on your camera, but some lenses feature a ring which volition allow you manually select what discontinuity will be selected.
Zoom lenses versus Prime number lenses
Nosotros've already mentioned zoom lenses, which take adjustable focal lengths. Lenses that don't zoom are called 'prime' lenses: if you need to put more than or less of a scene into your frame, you'll need to modify your position or change lenses altogether. By and large, prime number lenses are less costly than zoom lenses, considering they don't take to be as complicated. Prime lenses also typically offering a larger maximum discontinuity setting than zoom lenses and can do so without being very large.
Autofocus
Up until the early 1980'southward you were focusing a photographic camera lens past yourself: automatic focus wasn't really prominent until 1977, and even so, it was tedious and inconsistent. Today, camera lenses can focus quickly, nearly-silently, and tin can accurately focus consistently, even in sub-optimal conditions. Many lenses aren't really designed with manual focus in heed, with thin manual focus rings that don't accept a lot of fidelity for small adjustments. There are companies, even so, offer lenses without automatic focus, but it volition be upwards to y'all decide whether y'all demand the feature.

The Bower 8mm f/3.5 fisheye lens costs just over $200, while the Carl Zeiss 135mm f/2 APO Sonnar lens costs just over $2,000. Neither lens has autofocus.
Categories of lenses
There is a jungle of lenses out there, and the choice tin announced to be overwhelming. Fortunately, the dissimilar lenses are created for unlike purposes and are generally divisible into four categories.
Wide Angle lenses
A lens that has a focal length of 24mm or less is generally considered to be a wide-angle lens. Wide-angle lenses capture more than of the scene, which makes them ideal for and so-called 'landscape' photography. Imagine a huge mountain vista, the wide open African Serengeti or a massive waterfall: A wide-angle lens is a skillful selection for all these shooting scenarios. Wide-angle lenses are also expert choices when shooting indoors, particularly if y'all want to capture all of an indoor scene similar a 200 year-old cathedral in Europe. Finally, broad-angle lenses are not bad for emphasizing a foreground subject: Shoot broad and make it close, and your subject field will dominate the frame.
Wide-bending lenses come in 2 flavors: rectilinear and fisheye. A lens which uses a rectilinear blueprint seeks to endeavor and keep the proportion and perspective of a scene in a way that'south accurate to reality. A fisheye lens doesn't effort this, simply allow the optic to warp what y'all see in whatever way in order to fit it into the scene.

Two scenes shot from the same location. On the left, shot with a 16mm fisheye lens; on the right, shot with a 17mm rectilinear lens.
Standard lenses
A lens that falls in the range between 35mm and 60mm is generally thought of as a standard lens, considering the pictures they take tend to friction match the style scenes await to our optics. This range is the workhorse for most photographers, providing a natural perspective for lots of shooting scenarios.
Telephoto lenses
A lens that is longer than 70mm is generally considered a telephoto lens. Telephotos lenses magnify the scene to bring objects closer to the lensman. Non but do telephoto lenses make faraway objects appear closer, just they also makes objects announced closer together. Because y'all can't get onto the field with the other athletes, telephoto lenses are a must for photographing most sports.

A wide-angle (24mm eq.) view on the left compared to a telephoto view (200mm eq.) on the correct.
Special Purposes lenses
The categories above cover well-nigh 95% of all the lenses created, only even then, there are a few other, generally more expensive lenses which exist for specific purposes.
Portrait lenses
A lens with a focal length between 85mm and 135mm, with a fast aperture, is a popular choice to shoot portraits. Some portrait lenses come with special features to control out-of-focus elements in the photograph, as well. Ever wonder why that professional photo taken at your friend's wedding is more flattering than your latest selfie? The pro probably used a telephoto 'portrait' lens, rather than the broad-angle focal length used for your selfie.
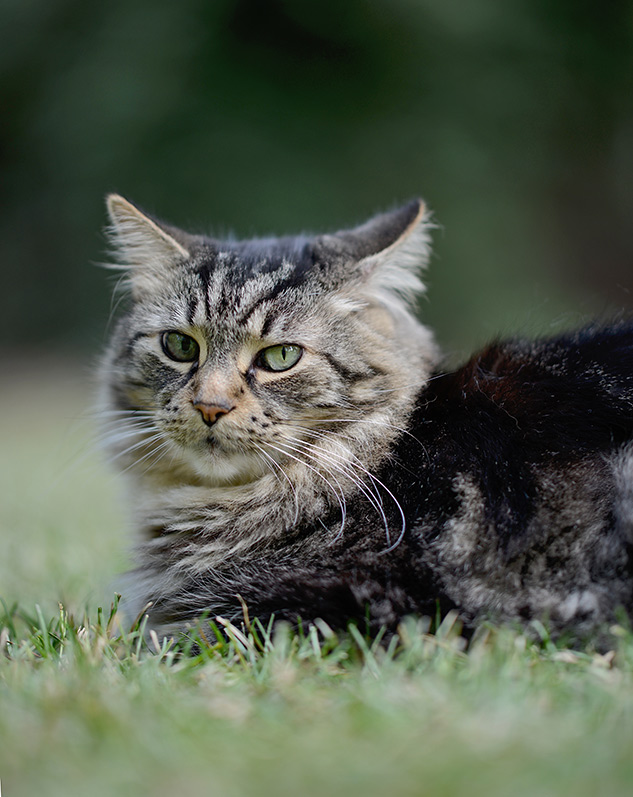

Portrait Lens: The Nikon 105mm f/ane.iv, show hither for example, offers a longer focal length for minimal subject distortion and a vivid aperture for smooth, blurry backgrounds and corking "subject isolation."
Macro lenses
A lens which is designed specifically to magnify objects nearby is referred to as a macro lens. Macro lenses come in a diverseness of focal lengths, but generally come equipped with special features to help with the precise focusing that'southward required in taking a expert photograph of a pocket-size object. What makes a lens 'macro?' The nearly intuitive feature is the 'minimum focus distance,' which is the closest an object can exist to the camera and still be in focus... any closer and things become blurry. A lens designed for working at macro distances may have special features like focus limiters and special focusing modes.
Macro lenses can exist used for other types of photography, but are more often than not larger, heavier and more expensive than a similar lens not optimized for macro photography.
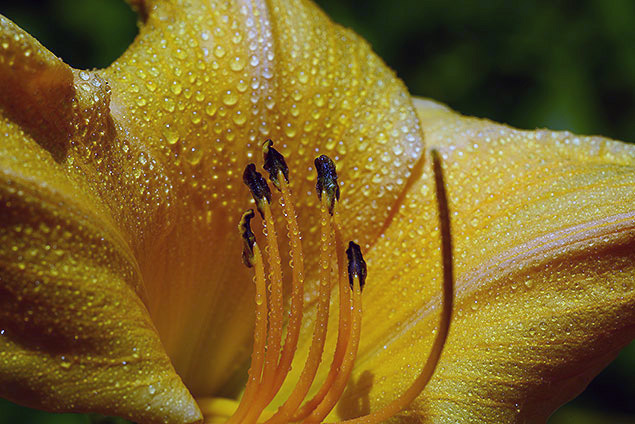

Macro lenses, such every bit the Tamron 90mm f/ii.8, lets you focus very close to your subject.
Tilt-Shift lenses
These special lenses allow a photographer to arrange the plane of focus in their scene. You might be interested in this kind of lens if you photo a lot of buildings and are concerned well-nigh making the angles of the building run parallel to the side of the image. As well, you can create a "miniature" outcome which blurs the top and bottom parts of an image, as shown in the example below.
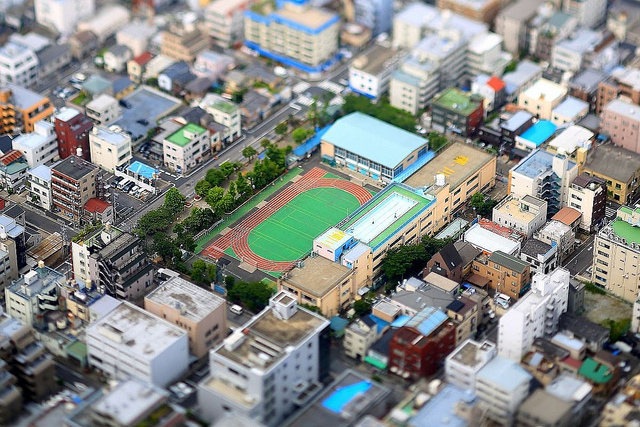

Special Lens Technologies
Some lenses offer more features than others, by and large making them more expensive, just also provide a better or more sophisticated shooting experience for the photographer. Different manufacturers have different names for some of these technologies, but generally, they all eddy downward to unlike ways of saying the same matter.
The most common technology making its manner into lenses today is image stabilization. Property a camera steady and then that y'all can take a crisp, abrupt photograph of a subject can be an art, especially if the camera and lens counterbalance several pounds. Image stabilization is a engineering science where ane of the elements of a lens is gyroscopically stabilized, compensating for the hand-holding motion of the photographer.



Prototype Stabilization On (left) vs. Image Stabilization Off (right)
Image stabilization used to exist found only in the most expensive lenses, but improvements in the applied science have seen it being implemented in fifty-fifty relatively economical ones as well. However, it'due south worth noting that no amount of epitome stabilization will stop your subject from moving around.
Another technology of note is quiet autofocus. When digital cameras started beingness able to record movies, the sound of a lens focusing all of a sudden became an outcome, as information technology was loud plenty to be picked up by the microphone in the photographic camera. All the manufacturers have become aware of this, and newer lenses now have more than mod autofocus systems, which are both extremely serenity and can also support improved continuous autofocus, like you would find in a regular video camera.
Finally, some contempo lenses also include features you'd ordinarily see in a dedicated video camera, similar ability zoom. With this feature, the photographer is able to adapt the zoom of the lens smoothly and at a consistent speed: this kind of thing is bully for movie-making.
Conclusion
We've covered a lot of basis in this article. In that location's no such affair equally a perfect lens, equally they are all different in their own subtle ways. The nigh important thing is finding the lens or lenses that match your shooting style: often times a photographer doesn't get the images they want because they're not shooting with the right lens. Hopefully, this article has helped you get started to find exactly what yous need!
(Tilt-shift instance prototype courtesy of Koji Nakaya/ pinboke_planet / Flickr; used nether a Creative Commons CC-BY-ii.0 license. )

A wide-bending (24mm eq.) view on the left compared to a telephoto view (200mm eq.) on the correct.
Source: https://www.imaging-resource.com/articles/camera-lenses-101-an-introduction-to-camera-lenses
Posted by: moorehiment.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Know What Camera Lens To Have"
Post a Comment